Grid-Connected Boost-Half-Bridge Photovoltaic Micro
Jul 23, 2024 · Abstract—This project presents a grid-connected boost half- bridge photovoltaic (PV) micro inverter system and its control implementations. A full-bridge pulse width-

An Integrated Boost Micro-inverter for PV Generation System
Apr 17, 2022 · This paper proposed an integrated boost micro-inverter (IBMI) that adapts MOSFETS without reverse recovery problem of their body diodes. Only two active switches

New Start-up Schemes for Isolated Full-Bridge Boost
May 12, 2020 · Two new start-up schemes for the active-clamp type isolated full-bridge boost converters are proposed in this paper. The control timing for each scheme, which are

Boost Half-Bridge micro-inverter. | Download
The boost-bridge micro-inverter is shown in figure 5 is composed of two decoupled power processing stages [8] [9] the forward dc-dc converter. a

800VA Pure Sine Wave Inverter''s Reference Design
Apr 1, 2023 · The pure Sine Wave inverter has various applications because of its key advantages such as operation with very low harmonic distortion and clean power like utility-supplied

GRID CONNECTED PHOTOVOLTAIC MICRO INVERTER
Sep 1, 2024 · A boost-half-bridge and full bridge micro inverter for grid-connected PV systems has been presented. The minimal use of semiconductor devices, circuit simplicity, and easy

Soft-switching buck/boost full-bridge three-port converter
May 1, 2023 · In this paper, a new structure for a DC-DC full-bridge buck/boost LLC three-port converter (TPC) is proposed. The configuration of the converter is designed using the

(PDF) Microinverter Topology based Single
Aug 1, 2018 · This paper discussed the topology development of a single-stage microinverter in grid-connected PV system. In general, the microinverter

Grid connected Boost-Full-Bridge photovoltaic
Jan 24, 2014 · This project presents a novel grid-connected Boost full-bridge Photovoltaic (PV) micro inverter system and its control implementations. The operating principles and dynamics

Boost Voltage Single Phase Full Bridge Inverter with No
Aug 22, 2022 · The full-bridge switches work at low frequency; the other switches work at high frequency. The inverter uses two capacitor modules to charge and discharge alternately so as

Full-Bridge Single-Inductor Based Buck-Boost Inverter
May 26, 2023 · To compensate for the variations of voltage, a buck-boost power conditioning system can be used. This paper presents a full-bridge single-inductor based buck boost

GRID-CONNECTED PHOTOVOLTAIC POWER SYSTEM USING BOOST HALF
In this paper, a novel soft-switching isolated full bridge dc-dc converter with voltage quadruple as a front-end converter-based inverter is being proposed. It has only four primary devices with

Low cost transformer isolated boost half-bridge micro-inverter
Feb 1, 2012 · Request PDF | Low cost transformer isolated boost half-bridge micro-inverter for single-phase grid-connected photovoltaic system | This paper presents a low cost high

Photovoltaic micro-inverter with front-end DC-DC converter
Jun 6, 2013 · A photovoltaic micro-inverter with a half-bridge inverter, half-wave cycloconverter and front-end boost converter is proposed with a series resonant circuit. A

Dual Active Bridge based Micro-Inverter for Standalone Renewable Energy
Dec 19, 2020 · Micro-inverters are required to interface PV generation directly with AC loads or grid at low power levels. A typical microinverter consists of a DC/DC conversion stage,

PV-Fed Micro-Inverter with Battery Storage for Single Phase
Apr 5, 2023 · Abstract Nowadays, micro-inverters are trending due to the latest features consisting in PV technology. However, integration of a high-gain boost converter is needed to

Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Power System Using Boost
Oct 15, 2013 · alf-bridge micro inverter for grid-connected PV systems has been presented. The minimal use of semiconductor devices, circuit simplicity, and easy control, the boost-half-b

Compact Single-Stage Micro-Inverter with Advanced
Mar 31, 2019 · This paper proposes a grid-connected single-stage micro-inverter with low cost, small size, and high efficiency to drive a 320 W class photovoltaic panel. This micro-inverter

JETIR Research Journal
Sep 26, 2023 · The topology presented in [9] is a boost converter in combination with a half bridge inverter and coupled inductors which are used to improve the output voltage gain of the inverter.

Reduction of input voltage/current ripples of boost half-bridge
Aug 1, 2019 · This paper describes a boost half-bridge DC-DC converter for photovoltaic system that reduces the input voltage and current ripples by using a 1:1 transformer and an auxiliary

Single power-conversion DAB microinverter with safe commutation and
Nov 15, 2019 · This paper presents a single power-conversion dual-active-bridge (DAB) microinverter with safe commutation and high efficiency for PV power applicatio

Low cost single stage micro-inverter with MPPT for grid
Aug 2, 2025 · Grid-connected boost-half- bridge photovoltaic micro-inverter system using repetitive current control and maximum power point tracking. IEEE Transactions on Power
Overview of micro-inverters as a challenging technology in
Feb 1, 2018 · In [25], a boost-half-bridge DC–DC converter is combined with a full-bridge pulse width-modulated inverter. The developed topology provides high power factor and very low

(PDF) Grid-tie pv microinverter with isolated full
Sep 5, 2015 · The full-bridge boost converter used in this work is intended to be used as the firs t stage of a grid-tie inverter based on the classical converter

Full-Bridge Single-Inductor Based Buck-Boost Inverter
May 26, 2023 · Based on the proposed full-bridge inverter, a novel cascaded buck-boost inverter is also presented. It retains all the benefits of the proposed full-bridge inverter.

TI 10KW High efficient/small size solar inverter new
Jun 27, 2018 · Digital Isolation (ISO7842) & ISO5451) In-Design Isolated IGBT Driver Evaluation Platform for 3- Complete Micro-inverter design using SM72295 full Phase Inverter (1200V

Grid-connected boost-half-bridge photovoltaic micro inverter
Feb 9, 2012 · This paper presents a novel boost-half-bridge micro inverter and its control implementations for single-phase grid-connected photovoltaic systems. The proposed

Grid-Connected Boost-Half-Bridge Photovoltaic Micro
Dec 27, 2017 · The topology of the boost-half-bridge micro inverter for grid connected PV systems is depicted in Fig 1.The proposed circuit is composed of two decoupled power processing stages.

Review on novel single-phase grid-connected solar inverters:
Mar 1, 2020 · The ZVS topologies have been adopted to micro inverters with LC or LLC resonant converters following the DC-DC conversion stage where it comprises phase shifted full-bridge

Design of a Single-Stage Dual Active Bridge Microinverter
Feb 7, 2025 · This article presents an optimized design of a single-stage dual active bridge (DAB) dc–ac converter with off-grid load capability. DAB converters have attracted attention due to

Critical review on various inverter topologies for
Feb 22, 2021 · The paper is organised as follows: Section 2 illustrates the PV system topologies, Section 3 explains PV inverters, Section 4 discusses PV

Modeling and control of DC/AC converters for photovoltaic
Jan 1, 2021 · This paper is devoted to the modelling and control for a low cost, high-power quality single-phase voltage source inverter (VSI) for a grid-tied PV-based micro-inverter system. The

Reduction of input voltage/current ripples of boost half-bridge
Aug 1, 2019 · Therefore, a boost half-bridge (BHB) converter with the advantages of circuit simplicity and high ηe is used as a typical DC-DC converter for the micro-inverter (Jiang et al.,
Grid Connected Boost-Full-Bridge Photovoltaic Micro
Apr 17, 2014 · This paper presents a novel Grid-connected Boost full-bridge photovoltaic (PV) microinverter system and its control implementations. This project is a demonstration model of

Research and design of a dual buck micro grid-connected inverter
Apr 1, 2025 · Smart grids have spurred the development of small-scale photovoltaic power generation, with micro inverters becoming the preferred choice for such systems due to their

Grid-connected Photovoltaic Power System Using Boost
May 24, 2025 · A boost-half-bridge micro inverter for grid-connected PV systems has been presented. The minimal use of semiconductor devices, circuit simplicity, and easy control, the

6 FAQs about [Micro inverter full bridge boost]
What is a boost-half-bridge micro inverter for grid connected PV systems?
The topology of the boost-half-bridge micro inverter for grid connected PV systems is depicted in Fig 1.The proposed circuit is composed of two decoupled power processing stages. The conventional boost converter is modified by splitting the output dc capacitor into two separate ones.
What is a microinverter & how does it work?
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Microinverters are a growing and rapidly evolving part of the photovoltaic (PV) system. Modern microinverters are designed to convert the DC power from one PV module (solar panel) to the AC grid, and are designed for a max output power in the range of 180W to 300W.
What is a boost-half-bridge DC-DC converter?
In order to achieve low cost, easy control, high efficiency, and high reliability, a boost-half-bridge dc–dc converter using minimal devices is introduced to interface the low-voltage PV module. A full- bridge pulse width-modulated inverter is cascaded and injects synchronized sinusoidal current to the grid.
What is a DC-link microinverter?
These topologies use a DC/DC converter with a high boost ratio to boost from the PV module voltage to the intermediate DC-bus voltage, and then use a conventional PWM controlled MOSFET or IGBT full-bridge to invert the waveform to the grid. This type of microinverter is also referred to as a DC-link topology (see ).
What is a single-stage microinverter?
Though perhaps not the most accurate name, this category of microinverter topologies is often referred to as a “single-stage microinverter”because the boosting of the panel voltage and shaping of the AC waveform is accomplished in a single stage.
What is unfolding microinverter?
The unfolding inverter is generally implemented with 4 SCR’s (silicon controlled rectifiers) that switch at the grid frequency. The DC/DC stage can be implemented as a quasi-resonant interleaved flyback or another topology. Figure 1. Block Diagram of Microinverter Using a Single-Stage Topology
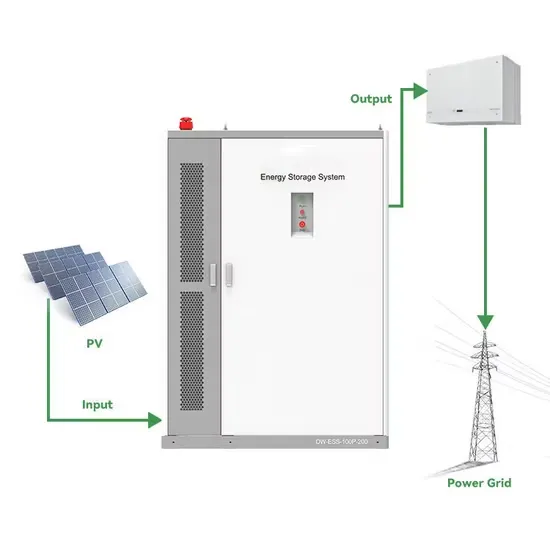
Industry Information
- Use of DC power supply for outdoor use
- Photovoltaic power station energy storage site energy
- Top 10 Energy Storage Projects in Nicosia
- Kosovo New Energy Battery Cabinet Factory
- Advancedness of Photovoltaic Curtain Wall
- How much power does a portable outdoor power supply have
- Which brand of 12v to 220v inverter is good
- Hot sale 5kva inverter system for sale distributor
- Vaduz 5g base station changes to direct power supply
- What is the general power ratio of photovoltaic panels
- Home battery storage in China in Karachi
- Hot sale 50kw sunsynk inverter factory exporter
- Single compressed air energy storage project
- Dual output portable power bank
- Riga Off-Grid Inverter
- Costa Rica Energy Storage Battery Wholesale Manufacturer
- South African home energy storage manufacturers supply
- Huawei established an energy storage battery factory
- Tirana monocrystalline photovoltaic panel price
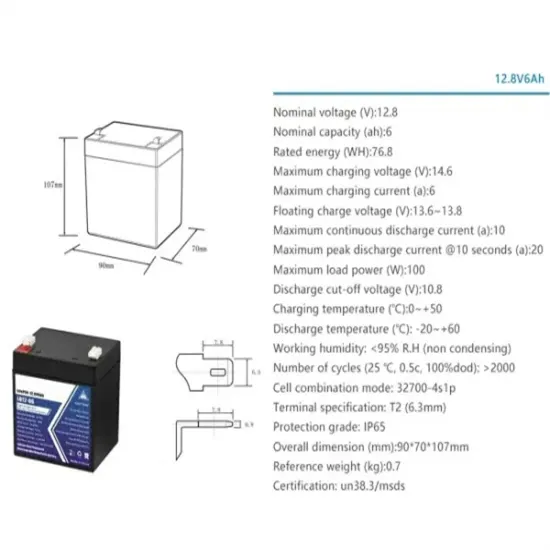
- Cylindrical and square lithium batteries
- Amman small photovoltaic panel manufacturer
- Old circuit breaker in China in Singapore
- Benefits of distributed energy storage in Ljubljana
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

