Effect of changing the length of an inverter''s N-mos
Dec 13, 2016 · After checking it a bit, I arrived at the following answer: Increasing the length of the N-mos means that the current will take more time to pass the tunnel, effectively let''s say that

Does the increasing of supply voltage, for a
Oct 25, 2016 · @Andyaka The role of the ac inverter is only the protection, as you know there is some limiting parameters like maximum output voltage and

Solar Voltage Rise – why you should care
May 13, 2019 · Solar voltage rise can significantly reduce solar production. Learn why it happens and how to calculate voltage rise. Discover 4 key ways to

2. Theory
Aug 30, 2024 · The voltage drop becomes larger when the current increases. This is the case when an inverter is loaded with maximum load or when a battery charger is charging at full

If you decrease the voltage, will the current increase?
Learn how voltage, current, and resistance are related to one another. Explore the relationship between voltage and current, as described by Ohm''s law.

Does Current Decrease When Voltage Increases?
Jan 24, 2024 · According to Ohm''s Law, Current Increases when Voltage increases (I=V/R), but Current decreases when Voltage increases according to (P = VI) formula. Why does

If you decrease the voltage, will the current increase?
No, decreasing the voltage will not increase the current. In fact, according to Ohm''s Law, current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance, which can be

What happens to current and voltage when resistance increases?
Oct 12, 2022 · According to Ohm''s Law, Current Increases when Voltage increases (I=V/R), but Current decreases when Voltage increases according to (P = VI) formula. Does current

Why does lowering VDD increases the delay for digital circuits?
Jul 14, 2021 · CMOS loads are largely capacitive, so the amount of current you deliver directly affects the rate at which that node can change voltage...hence, the circuit is slowed down.

delay on cmos inverter while increasing W of
Apr 28, 2014 · We have one CMOS inverter and a fixed capacitance as load, for example 0.1pF . As an experiment we increase W of nMOS and pMOS and

lect4.ppt
Mar 2, 2020 · Sketch a 3-input NAND with transistor widths chosen to achieve effective rise and fall resistances equal to a unit inverter (R). Annotate the 3-input NAND gate with gate and

Why the input capacitance value decrease as the
Oct 5, 2020 · Following is the screenshot of the logic CMOS-inverter curve (Input capacitance vs voltage). Why the input capacitance decreases with the

Why in a inverter DC to AC 12V et 220V when I increase the voltage
Jun 20, 2024 · Power is Voltage times Current, so if the transformer or inverter increases the voltage, it must also decrease the current to maintain the same power. Similarly, if a

Why DC supply voltage is increasing when
Mar 31, 2024 · 0 If I connect my inverter to a resistive load or small inductive load the DC supply voltage (in my application it is 56 V) stays constant. However, if

If you decrease the voltage, will the current increase?
When you decrease the voltage while keeping the resistance constant, the current will decrease. For example, if you have a circuit with a resistance of 10 ohms and you reduce the voltage

Why does the current rise and fall linearly in a DC-DC
Jan 9, 2015 · In that case, your inductor voltage will equal the supply voltage (when the switch is on) or the supply voltage minus the load voltage (when the switch is off). The latter voltage is

5. CMOS Gate Characteristics
Sep 10, 2020 · 3If the supply voltage of a chip increases, the maximum transistor current willincrease 4If the width of a transistor increases, its gate capacitance will increase 5If the

Will reducing inverter output voltage during
Jan 13, 2024 · The difference will by minimal depending on the base load, but using a lower voltage means your Amps increase and your battery has X

How does an increase in operating frequency result in decrease
Dec 1, 2013 · I was reading about inverters in a textbook where the author says that The size and cost of the circuit can be reduced to some extent if the operating frequency is increased but

Solved 1) If the width of a transistor increases, the | Chegg
Question: 1) If the width of a transistor increases, the current will increase decrease not change 2) If the length of a transistor increases, the current will increase decrease not change 3) If the

Why does the current THD increase and voltage
Jan 4, 2023 · I have a three phase inverter model and I am investigating the effects of an increased switching frequency for pre-defined LC filter

The Inverter
An approximation can be obtained by replacing the time-varying charging current by a fixed current I av . This is the average of the currents at the end points of the voltage transition.

Why does decreasing the CMOS supply voltage
Feb 17, 2021 · Fig 5.12 b is the voltage transfer characteristic of a CMOS inverter for the supply voltages of 200 mV, 100 mV, and 50 mV (while keeping the

How does increasing voltage or current affect the power?
Jul 16, 2025 · The power will remain the same for a particular load as we are not changing the load. so if we increase the voltage, the current will decrease to make the net power consumed

Why Voltage Matters
Jun 12, 2025 · Because raising the voltage reduces the current needed to deliver a given amount of power, the resultant lower current reduces I²R (a formula for

Why does high temperature increase delay of
Nov 8, 2022 · The delay increases at high temperature because carrier mobility . The decrease in carrier mobility causes a larger effect on drain current than
Given Ohm''s law, how can current increase if
Jul 16, 2025 · So if the voltage increases, then the current increases provided that the resistance remains constant. I know that Voltage or potential difference

According to the Ohm''s Law, I ∝ V, But I ∝ 1/V
4 days ago · In I = V ÷ R, Current is Directly Proportional to the Voltage, But Current is Inversely Proportional to the Voltage in P = V × I? This is another

Why Electric Motor Current Increases When Voltage Decreases
Apr 17, 2023 · They rely on a steady supply of electricity to function, with voltage and current playing key roles in their operation. But have you ever wondered why electric motor current

Why does increasing voltage result in a decrease in current
May 31, 2020 · I recently read that in order to conduct electricity over vast distances via power lines they had to step up voltage which results in a decrease in current through the medium.
Decreaseing voltage increases current
Apr 16, 2013 · If the length of a transistor increases, the current will increase decrease not change If the supply voltage of a chip increases, the maximum transistor current will increase...

Does Inverter Increase Electricity Bill?
Nov 17, 2023 · An inverter converts direct current (DC) from sources such as batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC). Its primary function is to

According to the Ohm''s Law, I ∝ V, But I ∝ 1/V
4 days ago · As we already know that in a step-up transformer, if voltage increases, the current decreases where power is same (as transformer only

If the current is increased, is there more charge flowing or is
Jul 17, 2025 · Problem Current is the amount of charge that is flowing through a component per unit of time. For a given voltage, Ohm''s law tells us that if we increase the resistance, then the
CMOS inverter delay
Apr 17, 2015 · How does the delay of a CMOS inverter decrease when we increase the supply voltage? What I thought was if we increase the Vdd from say, 1.8 to 1.9 volt, the output node

6 FAQs about [Will the current decrease if the inverter voltage increases ]
How does voltage affect current?
Unless you're talking about a Gunn diode or some other relatively esoteric device, an increase in voltage is seen with an increase in current. Volts = Current * resistance, so voltage is proportional to current with a coefficient of resistance. Ex: We have 5 volts going through a resistance of 0.5 ohms, what will the current be?
How does current increase and decrease according to Ohm's law?
According to Ohm’s Law, Current Increases when Voltage increases (I=V ÷ R), but Current decreases when Voltage increases according to (P = V × I) formula. How do you explain? i.e. According to Ohm’s Law: I ∝ V (Current directly proportional to the Voltage. I = V ÷ R)
How does voltage affect power consumption?
The power will remain the same for a particular load as we are not changing the load. so if we increase the voltage, the current will decrease to make the net power consumed by the load same as before. If we increase the current, the voltage will decrease for making the power same. The power will only change when we changes the load.
Does a decrease in voltage decrease current?
A decrease in voltage decreases current if all other factors remain constant. In an AC circuit a change in current can lead or lag a change in voltage. Could that be what is confusing you. what other factors would those be? In this case resistance.
What causes a voltage drop?
Remember that a voltage drop typically occurs during a high current event. The voltage drop becomes larger when the current increases. This is the case when an inverter is loaded with maximum load or when a battery charger is charging at full current. Load the inverter with maximum power.
How do you measure a voltage drop in an inverter?
The voltage drop becomes larger when the current increases. This is the case when an inverter is loaded with maximum load or when a battery charger is charging at full current. Load the inverter with maximum power. Measure the voltage across the negative cable between the inverter connection and the battery pole. Repeat this for the positive cable.
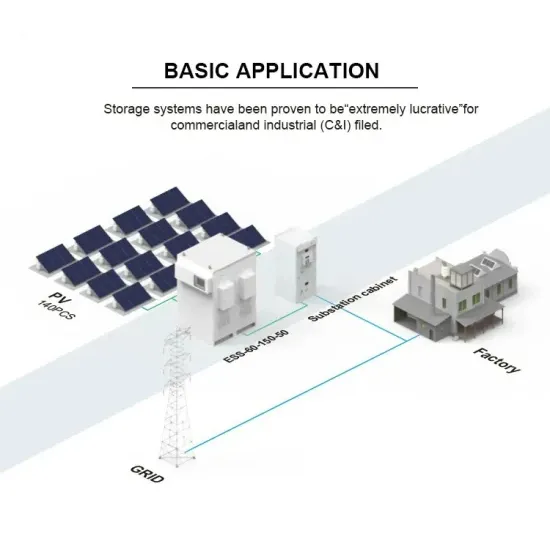
Industry Information
- 5g and 5g base stations for communication
- Container wireless signal base station
- Bidirectional portable energy storage prices in Azerbaijan
- Huawei energy storage equipment in Lyon France
- Solar photovoltaic panel columns
- 50kw inverter grid connection conditions
- Working mode of wind-solar hybrid system
- Kiribati Battery Energy Storage Solution
- Ladder Utilization of New Energy Battery Cabinets
- High quality 240 volt breaker in Abu-Dhabi
- BESS Uninterruptible Power Supply in Kuwait City
- Solar energy storage on-site without grid
- Paramaribo Trade Plaza Photovoltaic Panel Manufacturer
- Cheap wholesale replacing a breaker producer
- How big of an inverter can I use if the motor is 60w
- Nanya Photovoltaic Energy Storage Ratio
- Just right outdoor power supply function
- North America Photovoltaic Inverter
- Energy storage equipment manufacturing in Nigeria
- Is it good to use a generator in a container house
- Which is the best super capacitor in Nigeria
- Austria communication base station wind power photovoltaic power generation brand
- Micro new energy battery cabinet design
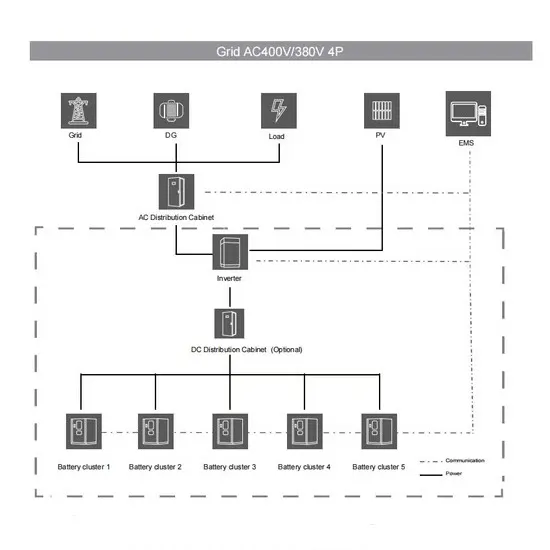
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
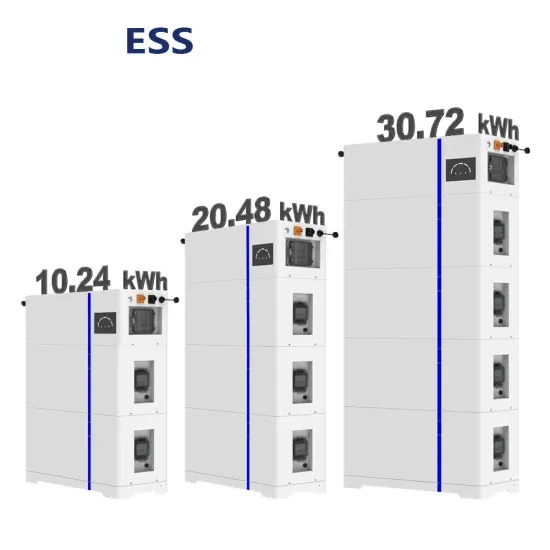
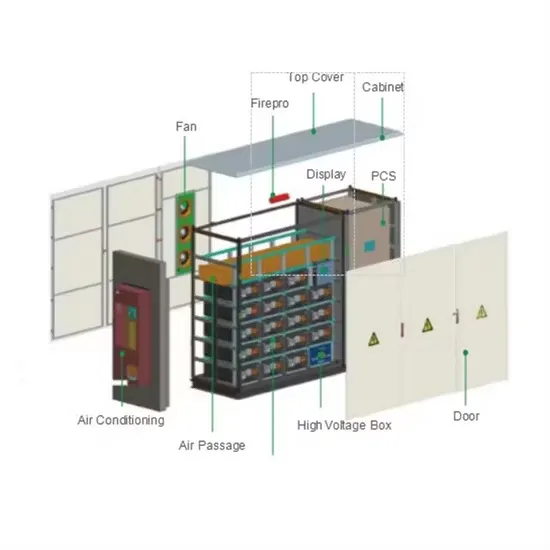
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.