A Review of Current-Limiting Control of Grid-Forming Inverters
Dec 8, 2022 · Grid-forming (GFM) inverters are recognized as a viable solution to increase the penetration of renewable energy in bulk power systems. However, they are physically different

Power Factor Control for Grid-Tied Photovoltaic Solar
Feb 23, 2012 · The main components of these systems are solar PV panels and PV inverters that convert dc power generated from the panels to ac power tied to the electric grid. This energy

Active/reactive power control of photovoltaic
Mar 12, 2018 · This paper proposes an analytical expression for the calculation of active and reactive power references of a grid-tied inverter, which limits the

Modeling and Studying the Impact of Dynamic Reactive
Dec 14, 2023 · MOdeling of power electronics inverters with current limiting strategies is important for understanding the transient fault response of the network, ensure system protection, and

Current Limiting Management in Grid Forming Inverter
In this section, the focus is on the development and implementation of a current limiting strategy designed to enhance the fault ride-through (FRT) capability of GFMI while mitigating all the
Advanced Current-Limiting and Power-Sharing Control in a PV-Based Grid
Jun 1, 2020 · Request PDF | Advanced Current-Limiting and Power-Sharing Control in a PV-Based Grid-Forming Inverter Under Unbalanced Grid Conditions | Grid-forming (GF) inverter

Modeling and studying the impact of dynamic reactive current limiting
Nov 1, 2023 · This paper leverages a comprehensive grid-following inverter with dynamic reactive current (DRC) limiting model. The inverter with DRC model is combined with distribution

Current limiting control method with adaptive virtual
Apr 1, 2023 · Current limiting is an important issue in the static synchronous compensator (STATCOM) with grid-forming (GFM) control. However, the conventional methods are difficult

Theoretical Comparison of Current Limiting Algorithms in Grid
Dec 18, 2024 · Grid-forming (GFM) inverters enable inverter-based resources to act as voltage sources, providing support to power systems. They are anticipated to serve as a technology

How to handle the current limiting of photovoltaic inverter
In this paper, an unbalanced fault current limiting strategy is proposed for the grid-connected inverter, which enables current limiting task under asymmetrical short circuit

Voltage Support Capability Analysis of Grid-Forming Inverters
Nov 8, 2024 · Voltage support capability is critical for grid-forming (GFM) inverters with current-limiting control (CLC) during grid faults. Despite the findings on the voltage support for

Grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Grid codes,
Jan 1, 2024 · With the development of modern and innovative inverter topologies, efficiency, size, weight, and reliability have all increased dramatically. This paper provides a thorough

Application Note
May 6, 2024 · Overview To improve grid stability, many electric utilities are introducing advanced grid limitations, requiring control of the active and reactive power of the inverter by various

Control of transient power compensation for virtual
Jan 1, 2025 · Leveraging the advantages of quasi-Z-source inverters, they are applied to VSG grid-connected systems, proposing an improved VSG control strategy tailored for quasi-Z

Advanced Current-Limiting and Power-Sharing Control in a PV-Based Grid
Dec 12, 2019 · Grid-forming (GF) inverter technology is a novel and evolving concept for systems with high penetration of renewables. The integration of these grid-independent units with the

Overcurrent_Limiting_in_Grid
Dec 6, 2024 · IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 39, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2024 14493 Overcurrent Limiting in Grid-Forming

Current limiting strategy for grid-connected
Oct 1, 2021 · This paper proposes an unbalance current limiting strategy for grid-connected inverters under asymmetrical short circuit fault conditions.

Fault Current of PV Inverters Under Grid
May 8, 2021 · As well as many benefits, many conflicts arise with the large-scale connection of distributed generation (DG) in distribution networks. Leading the

Current limiting strategies for grid forming inverters under
Sep 1, 2024 · Current limiting strategies can prioritize contribution during asymmetrical faults. Grid forming inverters are expected to play a key role in future power grids, replacing synchronous

A new control scheme for limiting the compensation current
Jan 1, 2022 · The proposed strategy inherently prioritizes the PV power injection over current harmonics filtering. It also considers the PV inverter''s rated capacity by characterizing it by its

Overcurrent Limiting in Grid-Forming Inverters: A
Sep 20, 2024 · Abstract—Grid-forming (GFM) inverters are increasingly rec-ognized as a solution to facilitate massive grid integration of inverter-based resources and enable 100% power

Advanced Current-Limiting and Power-Sharing Control in a PV-Based Grid
Dec 12, 2019 · Grid-forming (GF) inverter technology is a novel and evolving concept for systems with high penetration of renewables. The integration of these grid-independent

Current-Limiting Droop Control of Grid-connected
Mar 21, 2018 · Furthermore, this is achieved independently from grid voltage and frequency variations, maintaining the desired control performance under grid faults as well. Extensive

Overcurrent Limiting in Grid-Forming Inverters: A
Jul 18, 2024 · Grid-forming (GFM) inverters are increasingly recognized as a solution to facilitate massive grid integration of inverter-based resources and enable 100% power-electronics

Control strategy for current limitation and
To facilitate low-voltage ride-through (LVRT), it is imperative to ensure that inverter currents are sinusoidal and remain within permissible limits

(PDF) Current Source Inverter (CSI) Power
Oct 28, 2023 · Grid converters play a central role in renewable energy conversion. Among all inverter topologies, the current source inverter (CSI)

Optimal Control of Grid-Interfacing Inverters with Current
Mar 25, 2025 · In this paper, we directly focus on a nonlinear system that explicitly accounts for the saturation of the current magnitude. We use a Lyapunov stability approach to determine a

A new control scheme for limiting the compensation current
Jan 1, 2022 · Several recent studies have demonstrated the benefits of incorporating auxiliary functions such as power quality enhancement services in the control strategy of grid

Cross-Forming Control and Fault Current Limiting for Grid-Forming Inverters
Nov 18, 2024 · The cross-forming concept addresses the need for inverters to remain grid-forming (particularly voltage angle forming, as required by grid codes) while managing fault current

Low Voltage Ride through Control Capability of
Jan 1, 2019 · Abstract This paper presents the development and performance capability of a comprehensive Low voltage ride through (LVRT) control

Current Limiting Management in Grid Forming Inverter
In conclusion, this work has presented a comprehensive analysis of current limiting and power adjustment strategies for grid-forming inverters, particularly under fault conditions.

Current source inverter with grid forming control
Jan 1, 2024 · In this work, grid forming control using a PWM-CSI is proposed and the control structure is presented. The inverter possesses excellent current limiting characteristics since

Grid Forming Control of Grid-Connected Converters with
Feb 20, 2025 · By exploring the virtual impedance of inverters with virtual synchronous generator control and optimizing the virtual inertia and damping coefficient, an enhanced grid forming

Current-Limiting Control of Grid-Forming
Aug 9, 2022 · To protect the GFM inverters and support the power grid under faults or severe disturbances, various current-limiting control methods are

Fault-induced current limitation control for grid-forming inverters
May 1, 2025 · The method employs event-triggered time control logic that deactivates grid-forming inverter (GFMI)''s outer power control loop and uses the angle of the current reference as a

Overcurrent Limiting in Grid-Forming Inverters: A
Jul 18, 2024 · With this approach, we evaluate various performance criteria for different limiting methods, such as fault current contribution, voltage support, stability, and post-fault recovery.

6 FAQs about [Current limiting function of photovoltaic inverter in Belgian power grid]
Can fault induced inverters lead to overcurrents in a grid forming inverter?
Fault induced will lead to overcurrents in grid forming inverters. Current limiting strategies are classified into voltage and current-based strategies. Transient current, current contribution and stability will depend on the strategy. Transient enhancing strategies are used to ensure the stability during faults.
What are the goals of grid-connected PV inverters?
Under grid voltage sags, over current protection and exploiting the maximum capacity of the inverter are the two main goals of grid-connected PV inverters. To facilitate low-voltage ride-through (LVRT), it is imperative to ensure that inverter currents are sinusoidal and remain within permissible limits throughout the inverter operation.
Are current limiting and power adjustment strategies effective for grid-forming inverters?
In conclusion, this work has presented a comprehensive analysis of current limiting and power adjustment strategies for grid-forming inverters, particularly under fault conditions. The proposed control methodologies were tested using MATLAB Simulink to ensure their effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
How to provide voltage support in PV inverter?
To provide voltage support at the PCC, reactive power is injected into the grid under fault conditions as per the specified grid codes. As previously discussed, the simultaneous injection of peak active power from PVs and reactive power into the grid for voltage support can trigger the over current protection mechanism in PV inverter.
Does a two-phase and three-phase dip in grid voltage limit inverter current?
The results under two-phase and three-phase dip in the grid voltage shows that the proposed control strategy injects maximum reactive and active power and limits the inverter current by quickly activating the APC control loop during fault-ride-through period.
How do current limiting techniques affect GFM inverters?
As a result, they can profoundly impact device-level stability, transient system stability, power system protection, and fault recovery. This article offers a comprehensive review of state-of-the-art current-limiting techniques for GFM inverters and outlines open challenges where innovative solutions are needed.
Industry Information
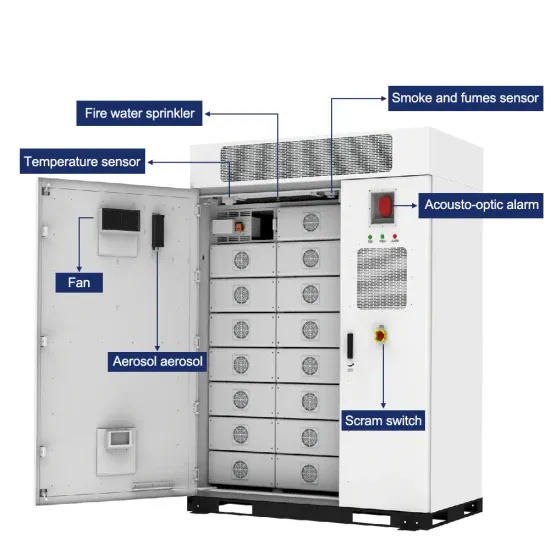
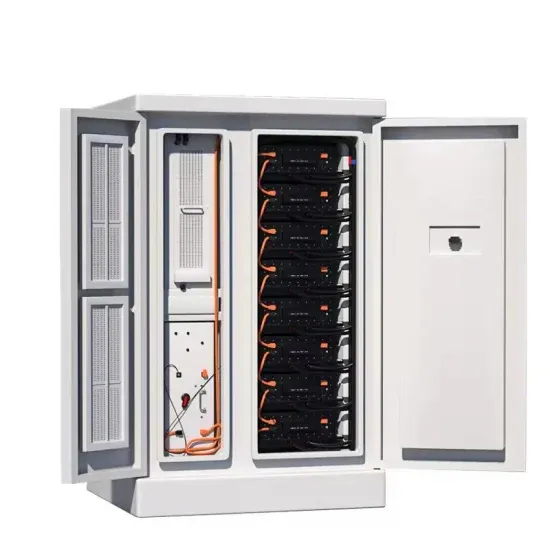
- Energy storage battery 5u and 3u
- DC side energy storage battery prefabricated cabin
- Communication base station EMS waterproof components
- Kathmandu solar wind and solar hybrid power supply system wholesale
- Factory price safety breaker in Estonia
- How much electricity does an industrial and commercial energy storage cabinet usually generate
- Generator switchgear for sale in Slovenia
- Malawi Photovoltaic Curtain Wall
- Is the photovoltaic inverter considered as weak current
- Communication next to the battery cabinet
- 500w photovoltaic panel
- Windhoek Grid Energy Storage Equipment
- Micro circuit breaker factory in Sao-Paulo
- Havana EK PV Inverter Sales
- Omega solar inverter in China in Monaco
- Efficacy of Industrial Energy Storage Batteries in Sri Lanka
- Super cheap capacitors
- How much current does a 12v inverter require
- Slovakia rooftop photovoltaic panel installation
- How to build a solar energy site
- Energy Storage System Implementation
- Manchester UK high cost-effective photovoltaic panel manufacturers
- Which Niamey Valley power storage equipment is the best
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

