Grid-Following Inverter (GFLI)
Jan 15, 2024 · Grid-Following Inverters (GFLI) and Grid-Forming Inverters (GFMI) are two basic categories of grid-connected inverters. Essentially, a grid

Improving Small-Signal Stability of Grid-Connected Inverter Under Weak
Jul 14, 2021 · The wide bandwidth of phase-locked loop (PLL) will increase the negative real part of the output impedance of the grid-connected inverter (GCI), thus destroying the stability of

Admittance Modeling and Stability Enhancement of Grid-connected
May 1, 2022 · In the renewable energy generation system, the phase-locked loop (PLL) for power grid synchronization plays a very important role, especially in weak grids. The asymmetric

Improving frequency stability in grid-forming inverters with
May 13, 2025 · The increasing integration of inverter-interfaced renewable energy sources (IIRES) has fundamentally changed the dynamics of current power systems, resulting in a significant

(PDF) A Comprehensive Review on Grid
Aug 13, 2020 · This review article presents a comprehensive review on the grid-connected PV systems. A wide spectrum of different classifications and

An Improved Repetitive Control Scheme for Grid-Connected Inverter
Jun 20, 2012 · The power quality of grid-connected inverters has drawn a lot of attention with the increased application of distributed power generation systems. The repetitive control technique

Grid Connected Inverter Reference Design (Rev. D)
May 11, 2022 · Description This reference design implements single-phase inverter (DC/AC) control using a C2000TM microcontroller (MCU). The design supports two modes of operation

Introduction to Grid Forming Inverters
Jun 18, 2024 · Why do we need Grid-forming (GFM) Inverters in the Bulk Power System? There is a rapid increase in the amount of inverter-based resources (IBRs) on the grid from Solar PV,

Grid-Forming Inverters: Shaping the Future of
Jul 5, 2023 · Grid-Forming Inverters: Their Impact on Stability, Resilience, and Integration The unintended separation of the grid due to equipment failures,

Passivity-Based Controller Design of PCC Voltage
Nov 14, 2023 · Abstract: The inherent resonance of LCL filter tends to result in the grid-connected inverter system oscillating due to the variation of the grid impedance at the point of common

A Frequency Adaptive Control Strategy for Grid-Connected Inverters
Nov 19, 2024 · For a grid-connected inverter (GCI) without ac voltage sensors connected to the weak grid, the occurrence of frequency variation diminishes the accuracy of the estimated grid

Hybrid compatible grid forming inverters with coordinated
Aug 16, 2025 · This guarantees that the inverter maintains stable operation in both grid-connected and islanded modes, effectively supporting frequency regulation, voltage control, and power

A Resilient Grid for a Renewable Future: How
May 21, 2025 · GFM Inverter: A Technological Answer to Grid Resilience Addressing the issue of grid resilience head-on is the Grid Forming (GFM)

SINGLE PHASE TRANSFORMERLESS INVERTER FOR GRID
May 19, 2022 · Abstract: Owing to the benefits of low cost, high efficiency, and light weight, transformerless inverters are widely used in grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) generation

Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study of
Jan 1, 2024 · Grid-forming inverters (GFMIs) are anticipated to play a leading role in future power systems. In contrast to their counterpart grid-following
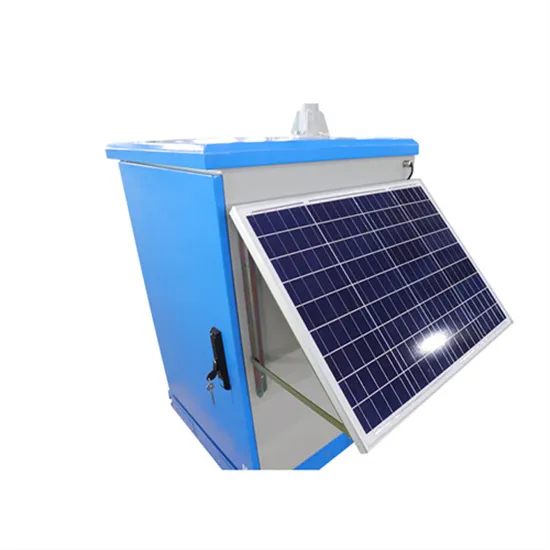

Fundamental‐Frequency Bus‐Impedance Analysis of Power
Jun 16, 2025 · Therefore, this article investigates how the placement of GFM and GFL inverters influences the equivalent fundamental-frequency impedance at different buses in a large-scale
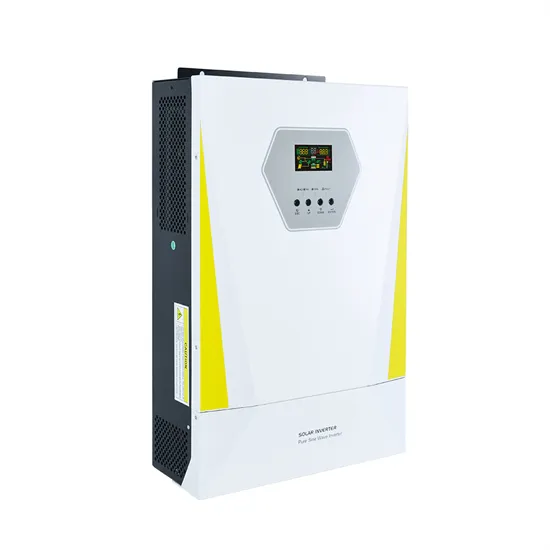

Frequency and Voltage Control Schemes for Three-Phase Grid
Jan 1, 2020 · We show that the proposed control architectures achieve both power sharing without a communication link, and desirable passivity properties that can enhance the dynamic
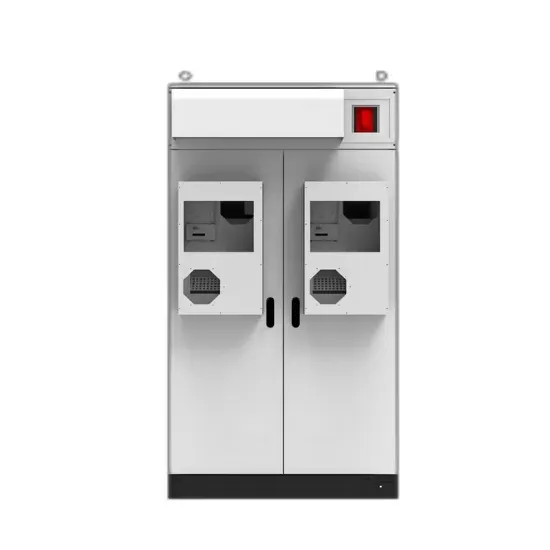

Grid Connected Inverter Reference Design (Rev. D)
May 11, 2022 · High-efficiency, low THD, and intuitive software make this design attractive for engineers working on an inverter design for UPS and alternative energy applications such as
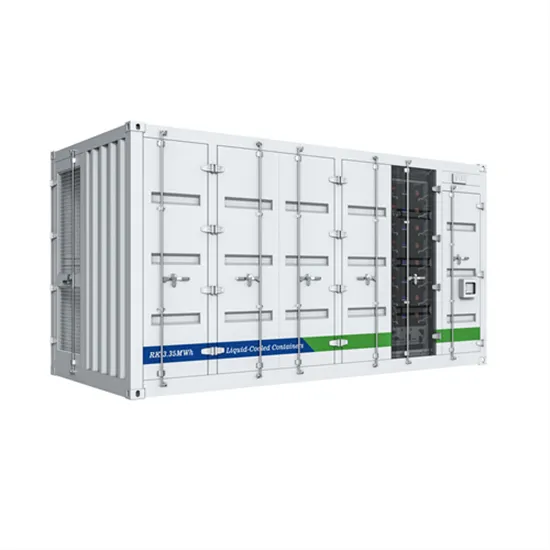

Neutral point clamped inverter for enhanced grid connected
May 29, 2025 · This research investigates a transformerless five-level neutral point clamped (NPC) inverter for grid-connected PV applications, aiming to overcome these challenges.

Online grid impedance estimation for grid-connected inverters
Mar 1, 2023 · Henry Shu-hung Chung, Chun-tak Lai, Xin Zhang and Weimin Wu, "Active cancellation of equivalent grid impedance for improving stability and injected power quality of

Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study
Mar 20, 2025 · Grid-forming inverters (GFMIs) are recognized as critical enablers for the transition to power systems with high renewable energy penetration.

A review of inverter topologies for single-phase grid-connected
May 1, 2017 · In this review work, some transformer-less topologies based on half-bridge, full-bridge configuration and multilevel concept, and some soft-switching inverter topologies are

Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study of
Jan 1, 2024 · Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study of Different Control Strategies in Frequency and Time Domains January 2024 IEEE Open Journal
Comparison of Voltage Control and Current
This study presents the comparative evaluation of the performance of the two main control techniques for Grid Connected Inverters. Sinusoidal Pulse Width

Grid Forming Inverter Modeling, Control, and Applications
Aug 13, 2021 · This paper surveys current literature on modeling methods, control techniques, protection schemes, applications, and real-world implementations pertaining to grid forming

Control of Grid-Connected Inverter | SpringerLink
May 17, 2023 · The control of grid-connected inverters has attracted tremendous attention from researchers in recent times. The challenges in the grid connection of inverters are greater as

First‐Order and High‐Order Repetitive Control
The modelling of a single-phase inverter is first introduced; then a first-order repetitive control is developed for the proposed grid-connected inverter.

A Frequency Adaptive Control Strategy for Grid-Connected Inverters
Nov 19, 2024 · For a grid-connected inverter (GCI) without ac voltage sensors connected to the weak grid, the occurrence of frequency variation diminishes the accuracy of the

Dispatching Grid-Forming Inverters in Grid-Connected
Sep 20, 2024 · The concept is validated with an example microgrid system with two GFM inverters, one diesel generator, one GFL inverter, and the load in both grid-connected and

Stability analysis of multi-parallel inverters with different
Apr 1, 2025 · In islanded mode, the inverters in the microgrid are usually connected with the load in parallel [5]. With the increase of the installed capacity of new energy, the traditional grid

Operating Principles of Grid-Connected Inverters
Sep 25, 2024 · Without the grid providing these references, the inverter would be unable to accurately adjust its output, and normal grid connection would not be possible. Enabling

(PDF) Disturbance Decoupling in Grid-Forming
Mar 25, 2025 · This paper presents a control strategy for grid-forming inverters, utilizing a cascaded dual-control scheme that integrates current and voltage

Stability analysis of distributed generation grid
Using grid impedance and the inverter output impedance model, the stability analysis method based on impedance is used to analyse the influence of grid

Inverter_documentation
Jul 9, 2024 · 2.2 Parameters General tab Number of aggregated inverters: Number of parallel-connected inverters Frequency: Grid frequency in Hz Inverter AC voltage: Voltage on the AC

Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study of Different
Mar 5, 2024 · Grid-forming inverters (GFMIs) are anticipated to play a leading role in future power systems. In contrast to their counterpart grid-following inverters, which employ phase-locked
Dispatching Grid-Forming Inverters in Grid-Connected
Sep 20, 2024 · This paper explores the dispatchability of grid-forming (GFM) inverters in grid-connected and islanded mode. An innovative concept of dispatching GFM sources (inverters

A review of single-phase grid-connected inverters for photovoltaic
Oct 31, 2005 · This review focuses on inverter technologies for connecting photovoltaic (PV) modules to a single-phase grid. The inverters are categorized into four classifications: 1) the

6 FAQs about [Industrial frequency inverter and grid-connected inverter]
What is a grid forming inverter?
As a result, grid-forming (GFM) inverters tors. Unlike GFLIs, voltage source behavior is emulated by of the internal voltage phasor . Consequently, GFMIs are akin to synchronous generators, even in weak grid scenarios. figured to operate in either islanded or grid-connected mode.
What is a grid-following inverter?
Grid-Following Inverters (GFLI) and Grid-Forming Inverters (GFMI) are two basic categories of grid-connected inverters. Essentially, a grid-following inverter works as a current source that synchronizes its output with the grid voltage and frequency and injects or absorbs active or reactive power by controlling its output current.
Are grid-forming inverters the future of power systems?
Research Council (Grant No.: DP230100801). ABSTRACT Grid-forming inverters (GFMIs) are anticipated to play a leading role in future power systems. In concept to form the voltage. Hence, they can not only stably operate in regions of the grid characterized by inertia support.
What is a power electronic inverter?
Unlike the synchronous generators in traditional power systems always performing as voltage-type apparatuses to the grids, the power electronic inverters can perform as either voltage- or current-type apparatus to the grids depending on their grid-forming or -following controls, as shown in Figure 1 [18 - 20].
What is the control design of a grid connected inverter?
The control design of this type of inverter may be challenging as several algorithms are required to run the inverter. This reference design uses the C2000 microcontroller (MCU) family of devices to implement control of a grid connected inverter with output current control.
What are the different types of power electronic inverters?
The power electronic inverter is further categorized into two types, i.e. grid-following (GFL) and grid-forming (GFM) inverters [8 - 10]. The GFL inverter is equivalent to a current source with high output parallel impedance, whereas the GFM inverter is equivalent to a voltage source with low output series impedance [11 - 13].
Industry Information
- San Diego Industrial Photovoltaic Panel Manufacturer
- Supply of charging inverter manufacturers
- Best power circuit breaker factory Factory
- Usb c power station for sale in Kuwait
- Angola Power Storage
- China dc breaker for solar in China producer
- High quality China upgrade circuit breaker company
- ASEAN Uninterruptible Power Supply Customization
- Kampala Civilian Solar Power Generation System
- 100 square meters of photovoltaic glass
- Budapest energy storage prices
- Photovoltaic Industrial and Commercial Site Energy Solar Energy
- Huawei outdoor power supply classification
- Photovoltaic inverter is heating up seriously
- Juba villa installs solar air conditioner
- 5g base station lithium battery power design
- Serbia high frequency inverter manufacturer
- 15 kWh energy storage cabinet
- Large rotating photovoltaic tiles
- Huawei Eastern Europe Photovoltaic Inverter
- Large cylindrical lithium battery life
- On grid inverter 5kw in China in Mexico
- Standby uninterruptible power supply long call
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

