A Brief Overview of Low-Frequency Power Inverters
Basic Principles and Characteristics of Low-Frequency Power Inverter A low-frequency power inverter is a power conversion system that converts direct

High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
Low-Frequency Inverters: Low-frequency inverters use heavy, iron-core transformers to step up the voltage from DC to AC. These transformers operate at the utility grid frequency of 50 Hz or

Technical comparison between Low Frequency
Aug 19, 2025 · What internal frequency the inverter circuits operate at – low frequency or high frequency (not to be confused with AC power output

Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
May 2, 2023 · Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for

Understanding Low Frequency Power Inverters
6 days ago · – Higher efficiency: Low frequency inverters typically exhibit higher efficiency than high frequency inverters, which can result in significant energy savings over time. – Lower

Low Frequency Inverter, High Frequency
Jun 5, 2020 · Low frequency inverter can withstand grid input conditions, such as voltage fluctuation, high voltage spike and lightning. However, the high
High Frequency Inverter vs Low Frequency Inverter: How to
Aug 18, 2025 · High frequency solar inverter first through the high-frequency DC / DC conversion technology, low-voltage DC inverter for high-frequency low-voltage alternating current; and

Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
Jul 25, 2025 · Yet, not all inverters are created equal. One of the most critical architectural decisions an engineer faces is the choice between a line-frequency (or low-frequency) and a

The Ultimate Guide to Low-Frequency Inverters
6 days ago · The adoption of low-frequency inverters over their high-frequency counterparts hinges on several compelling advantages. Their robust construction and low operating

High frequency inverter vs low frequency
Nov 2, 2023 · This article compares high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter from the aspects of working frequency, components, efficiency, size

Which is Better Low Frequency or High
3 days ago · Low frequency inverters are simpler, more robust and easier to control. High frequency inverters enable miniaturization, fast response,
Understanding the Difference Between Low
Mar 7, 2023 · With a low frequency output, usually 50Hz or 60Hz, these inverters provide the most effective option for powering more demanding appliances

How to Distinguish High Frequency Inverter and Low Frequency Inverter
Apr 11, 2024 · Low frequency inverter technique is similar to high frequency inverter technique, but produces AC power of a lower frequency and voltage level. Low frequency inverters use

The difference between low frequency inverter
Dec 22, 2021 · It first through the high frequency DC/DC transformation technology, the low voltage DC through the high frequency transformer boost,

Inverters
Understanding Low Voltage vs. High Voltage Inverters and Low Frequency vs. High Frequency Inverters. When setting up a solar energy system, choosing the right inverter is crucial.

Difference Between High and Low Frequency Inverter
Apr 30, 2025 · Low-frequency inverters can only invert the low-voltage DC of the battery into low-voltage AC (low-voltage inversion, so it can only be low-frequency inversion), and then boost it

Understanding inverter frequency – effects and
Oct 1, 2024 · The choice between a low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) inverter depends on various factors, including the application requirements,
Everything to Know Low Frequency Inverters
Low-frequency inverters, characterized by their use of transformers for electrical isolation, play a crucial role in a variety of high-reliability applications. This

Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters:
4 days ago · Low-frequency Inverters are designed to handle high-surge loads, typically 2-5 times their rated power output. This makes them perfect for

High Vs Low Frequency Inverters/UPS
Jul 1, 2023 · Why is a Transformer important in a Pure Sinewave Inverter/UPS? Isolation plays a major role in the functioning of the Inverter/UPS during the

DC‐link low‐frequency current and voltage
Nov 5, 2021 · Inverter''s performance and operating mode may be negatively affected by inverter input (dc-link) current and voltage ripple. It is a common

A High-Frequency Resonant Inverter Topology With Low-Voltage
Jul 31, 2008 · This paper presents a new switched-mode resonant inverter, which we term the inverter, that is well suited to operation at very high frequencies and to rapid on/off control.

SINAMICS Low Voltage Converters
6 days ago · The SINAMICS low-voltage drives include a power range from 0.12 to 6,600 kW to address a wide range of applications: from the most basic

Difference Between High and Low Frequency Inverter
Apr 30, 2025 · Let''s start with the simplest and most intuitive difference: low-frequency inverters have a large transformer built in, while high-frequency inverters have only a very small

Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters:
Feb 10, 2025 · What are high-frequency inverters? High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency

Voltage Fed Full Bridge DC-DC & DC-AC Converter High
Apr 1, 2023 · In many applications, it is important for an inverter to be lightweight and of a relatively small size. This can be achieved by using a High-Frequency Inverter that involves an
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Key
Aug 15, 2025 · Explore the key differences in low frequency vs high frequency inverters including their applications, advantages, and which is best for your

Understanding the Difference Between Low
Mar 7, 2023 · There are two types of inverters, low frequency and high frequency inverters. Inverters are used in solar power systems, wind turbines, and

What is the difference between a high frequency
Apr 25, 2024 · LOW FREQUENCY INVERTERThe low frequency inverter first inverts the DC power into a low frequency low-voltage AC power, and then

Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters:
Feb 10, 2025 · High-frequency inverters use high-frequency switches to convert incoming low-voltage DC power to high-frequency low-voltage AC power. This

High frequency verses low frequency inverters
Nov 26, 2022 · What is the difference between high, or low frequency inverters the pros and cons? I have seen a few posts someone said low was better for high surge load like AC units,

High Voltage High Frequency AC
MICNO high voltage inverter adopts the most mainstream power unit series technology, with DSP+ARM+FPGA three-core processor as the control core.

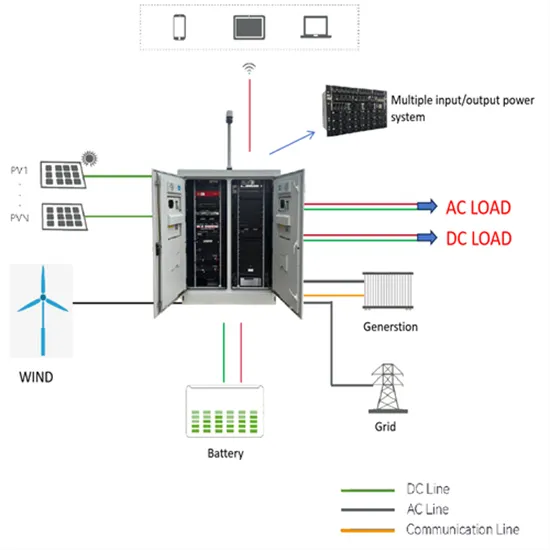
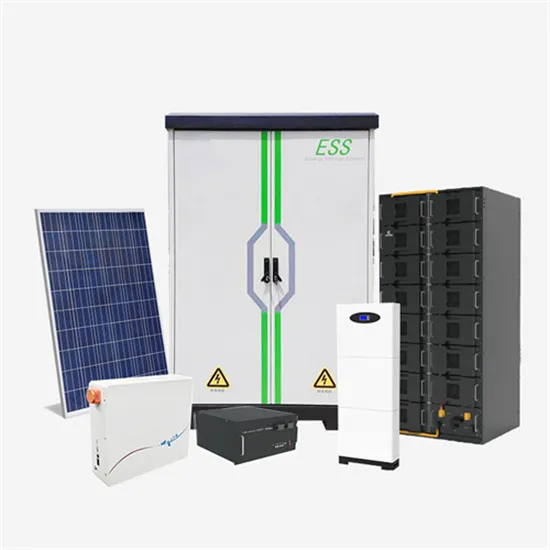
Inverters
Inverters Understanding Low Voltage vs. High Voltage Inverters and Low Frequency vs. High Frequency Inverters When setting up a solar energy system, choosing the right inverter is

Inverters, Types and Voltages
Dec 31, 2024 · Understanding Low Voltage vs. High Voltage Inverters and Low Frequency vs. High Frequency Inverters When setting up a solar energy system, choosing the right inverter is

6 FAQs about [Low frequency high voltage inverter]
What is the difference between low frequency and high frequency inverters?
Low-frequency Inverters are designed to handle high-surge loads, typically 2-5 times their rated power output. This makes them perfect for refrigerators, compressors, or air conditioners requiring extra power during startup. High-frequency inverters typically have 1.5-2 times their rated power, which limits their surge capacity.
What is a low frequency inverter?
Efficiency: Low-frequency inverters are known for their robustness and ability to handle high surge currents, making them suitable for powering heavy-duty appliances or equipment with high starting currents, such as motors and compressors.
What is a high frequency inverter?
Applications: These inverters are more suitable for off-grid systems where heavy loads and extreme conditions are expected, such as in industrial applications or in remote locations with harsh environments. Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers.
Should you buy a low-frequency inverter?
If you need to power appliances with high surge requirements, like refrigerators, compressors, or industrial machinery, a low-frequency inverter is a better choice due to its ability to handle high starting currents.
What are the disadvantages of a low frequency inverter?
Some drawbacks of low frequency inverters include: Large Size Slower Response Distortion Acoustic Noise Lower Efficiency Some limitations of high frequency inverters: Complexity EMI Issues Reliability Concerns Acoustic Noise Higher Cost Low frequency inverters are advantageous for: High frequency inverters are better for:
Why should you choose a high frequency inverter?
High frequency inverters enable miniaturization, fast response, efficiency and ultra-quiet operation. The choice depends on the specific size, performance, cost, reliability and noise criteria for the application. Hybrid inverters running at medium frequencies can balance the tradeoffs.
Industry Information
- New Delhi inverter 12v to 220v home use
- Chad lithium energy storage system prices
- Huawei power station energy storage device usage
- China-Europe Photovoltaic Inverter
- Photovoltaic flat tile roof
- Breaker distribution for sale in Yemen
- Wholesale lv switchgear panel in Burundi
- Connect the inverter to charge the battery
- Industrial switchgear factory in Uk
- Huawei Australia Sydney New Energy Storage
- Luanda energy storage container manufacturer
- How much is the price of aluminum acid energy storage battery in Zimbabwe
- Saudi Arabia hybrid energy 5G base station construction
- Solar power storage solutions in Russia
- Cheap 15kw hybrid inverter in China producer
- Yuenengda Energy Storage Outdoor Power Supply
- Acs automatic energy storage system
- How many kilowatt-hours of energy can be stored in a base station
- Photovoltaic battery energy storage costs
- Transparent solar panels photovoltaic power generation
- BESS a Singapore energy storage system manufacturer
- Energy Storage Smart Grid
- Battery cabinet base station power generation project
Commercial & Industrial Solar Storage Market Growth
The global commercial and industrial solar energy storage battery market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 400% in the past three years. Large-scale battery storage solutions now account for approximately 45% of all new commercial solar installations worldwide. North America leads with 42% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 30-35%. Europe follows with 35% market share, where standardized industrial storage designs have cut installation timelines by 60% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at 50% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 20% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-6 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $500/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Solar Battery Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving solar energy storage battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 50% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 20+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $1,000/kW to $550/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 40% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 30% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $450/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have improved ROI significantly, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-7 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $25,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $100,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

